-
[백준]17825: 주사위 윷놀이(java)Algorithm/백준 2022. 5. 15. 20:05728x90
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/17825
17825번: 주사위 윷놀이
주사위 윷놀이는 다음과 같은 게임판에서 하는 게임이다. 처음에는 시작 칸에 말 4개가 있다. 말은 게임판에 그려진 화살표의 방향대로만 이동할 수 있다. 말이 파란색 칸에서 이동을 시작하면
www.acmicpc.net
문제
주사위 윷놀이는 다음과 같은 게임판에서 하는 게임이다.
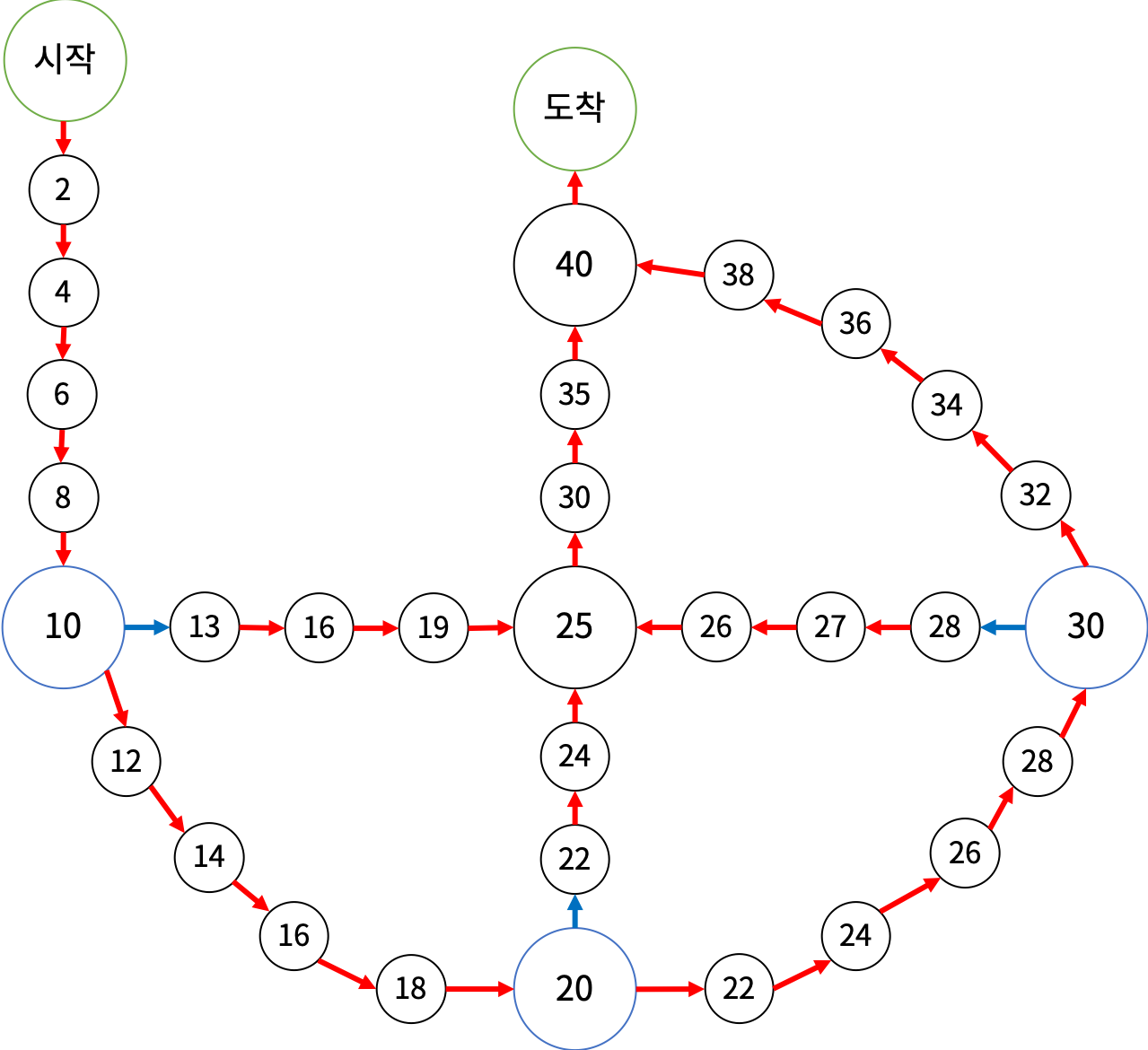
- 처음에는 시작 칸에 말 4개가 있다.
- 말은 게임판에 그려진 화살표의 방향대로만 이동할 수 있다. 말이 파란색 칸에서 이동을 시작하면 파란색 화살표를 타야 하고, 이동하는 도중이거나 파란색이 아닌 칸에서 이동을 시작하면 빨간색 화살표를 타야 한다. 말이 도착 칸으로 이동하면 주사위에 나온 수와 관계 없이 이동을 마친다.
- 게임은 10개의 턴으로 이루어진다. 매 턴마다 1부터 5까지 한 면에 하나씩 적혀있는 5면체 주사위를 굴리고, 도착 칸에 있지 않은 말을 하나 골라 주사위에 나온 수만큼 이동시킨다.
- 말이 이동을 마치는 칸에 다른 말이 있으면 그 말은 고를 수 없다. 단, 이동을 마치는 칸이 도착 칸이면 고를 수 있다.
- 말이 이동을 마칠 때마다 칸에 적혀있는 수가 점수에 추가된다.
주사위에서 나올 수 10개를 미리 알고 있을 때, 얻을 수 있는 점수의 최댓값을 구해보자.
입력
첫째 줄에 주사위에서 나올 수 10개가 순서대로 주어진다.
출력
얻을 수 있는 점수의 최댓값을 출력한다.
예제 입력 1
1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2예제 출력 1
190
풀이
맵을 어떻게 만들어야하지? 라는 고민을 제일 많이 하였다.
하지만 결론은 배열로 다 만들어두기(하드코딩..)을 선택하였다.
문제를 보면 길은 총 4개이다.
1) 가장 외각으로 도는길
2) 10 > 25 > 40 > 도착으로 가는 길
3) 20 > 25 > 40 > 도착으로 가는 길
4) 30 > 25 > 40 > 도착으로 가는 길
그것을 배열로 표현하였다.
- 이렇게 표현하였으므로 우리는 총 4군데의 종료지점 21, 30, 38, 47을 갖게되고, 같은 Point지만 다른 idx를 가질 수 있다.
static int [] map = { 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 30, 32, 34, 36, 38, 40, 0, //0 ~ 21 10, 13, 16, 19, 25, 30, 35, 40, 0, //22 ~ 30 20, 22, 24, 25, 30, 35, 40, 0, //31 ~ 38 30, 28, 27, 26, 25, 30, 35, 40, 0}; //39 ~ 47그 이후엔 우린 4개의 말이 있는데 그 말을 1, 2, 3, 4라고 할 때 중복 순열의 순서를 가질 수 있다.
ex) 4번을 뽑는다면 1, 1, 1, 1 / 1, 1, 1, 2 / 1, 1, 1, 3 등등..
중복 순열로 10번의 순서를 고르는 코드는 다음과 같습니다.
public static void permutation(int cnt) { if(cnt == 10) { playGame(); return; } for(int i=0; i<4; i++) { gamePiece[cnt] = i; permutation(cnt+1); } }10개의 모든 순서가 정해지면 playGame 함수를 통해 윷놀이 게임을 시작합니다.
playGame에서 게임을 시작하기전에 게임의 룰을 우선 살펴보겠습니다.
1) 이미 도착한 말은 움직일 수 없다.
2) 어떠한 말이 자리에있다면 그 자리로 갈 수 없다.
라는 특징이 존재합니다.
저는 이미 말의 순서를 고른 후 게임을 하였기때문에 불가능한 순서일 수 있습니다.
예를들어 1만 10번 play하는 경우에 1이 7번만에 도착을했다면 8, 9, 10번째 주사위는 아무것도 움직일 수 없으므로 불가능합니다.
playGema()함수는 아래와 같습니다.
public static void playGame() { boolean[] visited = new boolean[map.length]; int score = 0; int[] p = new int[4]; for(int i=0 ; i<10 ; i++) { int nowDice = dice[i]; int nowPiece = gamePiece[i]; if(isFinish(p[nowPiece])) return; int next = nextPoint(p[nowPiece], nowDice); if(isFinish(next)) { setVisited(visited, p[nowPiece], false); p[nowPiece] = next; continue; } if(visited[next]) return; setVisited(visited, p[nowPiece], false); setVisited(visited, next, true); p[nowPiece] = next; score += map[p[nowPiece]]; } ans = Math.max(ans, score); }- 이미 어떠한말이 자리하고있는지 확인하는 boolean형 배열 visited
- 현재까지의 점수를 누적하는 int형 변수 score
- 현재 각 말들의 postion이 어딘지 확인하는 배열 p를 선언하고 시작했습니다.
for문을 통해 총 10번의 주사위값을 적용시킵니다.
nowDice = 현재 주사위 번호
nowPiece = 현재 움직일 말 번호
if(isFinish(p[nowPiece]) = 만약 현재말이 이미 끝났다면? 위에 말한 1번 조건에 의해 이번에 골라진 순서는 불가능하므로 return 해줍니다.
next = nextPostiion(현재말, 현재주사위)로 next에 다음에 자리할 point를 찾아줍니다.
nextPoisiton() 함수는 아래와 같습니다.
public static int nextPoint(int nowIdx, int dice) { int nextIdx = nowIdx + dice; if(nowIdx < 21) { if(nextIdx >= 21) nextIdx = 21; } else if(nowIdx < 30) { if(nextIdx >= 30) nextIdx = 30; } else if(nowIdx < 38) { if(nextIdx >= 38) nextIdx = 38; } else if(nowIdx < 47) { if(nextIdx >= 47) nextIdx = 47; } if(nextIdx == 5) return 22; if(nextIdx == 10) return 31; if(nextIdx == 15) return 39; return nextIdx; }- 주사위가 맵을 넘어가면 종료지점에 자리하게 위치해줍니다.(배열때문에 종료지점이 총 4군데이다.)
- 현재 말의 위치 + 주사위 번호를 nextIdx에 넣어주고 nextIdx가만약 파란색 말판을 밟는다면 그 발판에 맞게 자리해줍니다.
이렇게 위치좌표가 구해졌다면 우리는
next가 종료지점이라면 우리는 현재 위치를 visited=false를 해주고 도착지점인 종료지점은 true처리 해주지 않습니다. (종료지점엔 여러개의 말이 존재해도 되기때문)
종료지점이 아니라면 현재 위치를 visited = false , 갈 위치를 visited = true처리 해줍니다.
visited를 체크함에있어 우리는 같은 자리이지만 다른 idx를 가질 수 있으므로 모든 경우를 다 체크해줍니다.
public static void setVisited(boolean[] visited, int idx, boolean check) { if(idx == 20 || idx == 29 || idx == 37 || idx == 46) { visited[20] = check; visited[29] = check; visited[37] = check; visited[46] = check; } else if(idx == 26 || idx == 34 || idx == 43) { visited[26] = check; visited[34] = check; visited[43] = check; } else if(idx == 27 || idx == 35 || idx == 44) { visited[27] = check; visited[35] = check; visited[44] = check; }else if(idx == 28 || idx == 36 || idx == 45) { visited[28] = check; visited[36] = check; visited[45] = check; }else { visited[idx] = check; } }지금까지 모두 통과되었다면 점수를 최솟값과 비교해 갱신합니다.
같은 자리들을 생각해주는게 조금 힘들었던 문제였던 것 같습니다.
전체 코드
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.util.StringTokenizer; public class BJ_G2_17825_주사위윷놀이 { static int [] map = { 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 30, 32, 34, 36, 38, 40, 0, //0 ~ 21 10, 13, 16, 19, 25, 30, 35, 40, 0, //22 ~ 30 20, 22, 24, 25, 30, 35, 40, 0, //31 ~ 38 30, 28, 27, 26, 25, 30, 35, 40, 0}; //39 ~ 47 static int[] dice = new int[10]; static int[] gamePiece = new int[10]; static int ans = 0; public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()); for(int i=0; i<10; i++) { dice[i] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); } permutation(0); System.out.println(ans); } public static void permutation(int cnt) { if(cnt == 10) { playGame(); return; } for(int i=0; i<4; i++) { gamePiece[cnt] = i; permutation(cnt+1); } } public static void playGame() { boolean[] visited = new boolean[map.length]; int score = 0; int[] p = new int[4]; for(int i=0 ; i<10 ; i++) { int nowDice = dice[i]; int nowPiece = gamePiece[i]; if(isFinish(p[nowPiece])) return; int next = nextPoint(p[nowPiece], nowDice); if(isFinish(next)) { setVisited(visited, p[nowPiece], false); p[nowPiece] = next; continue; } if(visited[next]) return; setVisited(visited, p[nowPiece], false); setVisited(visited, next, true); p[nowPiece] = next; score += map[p[nowPiece]]; } ans = Math.max(ans, score); } public static void setVisited(boolean[] visited, int idx, boolean check) { if(idx == 20 || idx == 29 || idx == 37 || idx == 46) { visited[20] = check; visited[29] = check; visited[37] = check; visited[46] = check; } else if(idx == 26 || idx == 34 || idx == 43) { visited[26] = check; visited[34] = check; visited[43] = check; } else if(idx == 27 || idx == 35 || idx == 44) { visited[27] = check; visited[35] = check; visited[44] = check; }else if(idx == 28 || idx == 36 || idx == 45) { visited[28] = check; visited[36] = check; visited[45] = check; }else { visited[idx] = check; } } public static int nextPoint(int nowIdx, int dice) { int nextIdx = nowIdx + dice; if(nowIdx < 21) { if(nextIdx >= 21) nextIdx = 21; } else if(nowIdx < 30) { if(nextIdx >= 30) nextIdx = 30; } else if(nowIdx < 38) { if(nextIdx >= 38) nextIdx = 38; } else if(nowIdx < 47) { if(nextIdx >= 47) nextIdx = 47; } if(nextIdx == 5) return 22; if(nextIdx == 10) return 31; if(nextIdx == 15) return 39; return nextIdx; } public static boolean isFinish(int idx) { return idx == 21 || idx == 30 || idx == 38 || idx == 47; } }728x90'Algorithm > 백준' 카테고리의 다른 글
[백준]2179: 비슷한 단어(javascript) (0) 2022.05.17 [백준]2138: 전구와 스위치(java) (0) 2022.05.16 [백준]16724: 피리 부는 사나이(java) (0) 2022.05.14 [백준]1041: 주사위(java) (0) 2022.05.13 [백준]11559: Puyo Puyo(java) (0) 2022.05.12